
Logs are essential in modern DevOps environments for debugging, monitoring, and maintaining the health of applications. Grafana Loki is a lightweight, cost-effective log management tool that can replace traditional log management software such as ELK. Loki is compatible with Grafana, Promtail, and other logging tools. This makes it the best log stack for Linux VPS environments.
This guide will show you how to install Grafana Loki, configure Grafana's visualization, and set up Promtail log collection.
How to Install Grafana Loki on a Linux VPS for Log Management
Grafana Loki, a log-aggregation tool inspired by Prometheus, is an aggregation software. It's optimized to store and query logs efficiently, without indexing all log content. Loki stores metadata in a separate location, which reduces storage and improves performance.
Grafana Loki is one of the easiest and most efficient ways to create a log management system that can scale. You get a powerful, lightweight logging stack that is suitable for both production servers and development environments.
Before installing Loki, ensure you have:
- A Linux VPS (Ubuntu/Debian/CentOS/AlmaLinux/RHEL)
- Root or sudo access
- Ports 3100 and 9080 (Loki) are allowed
- Grafana is optional but recommended
Step 1: Create a Dedicated Loki Directory
Create directories for Loki files and config files.
Loki is able to store log files, config files, and chunks of data.
Step 2: Download Loki Binary
Download the latest Loki Release:
Let’s get the executable permissions:
Loki is ready to go.
Step 3: Create Loki Configuration File
Create the main configuration file:
Copy the minimal Loki configuration:
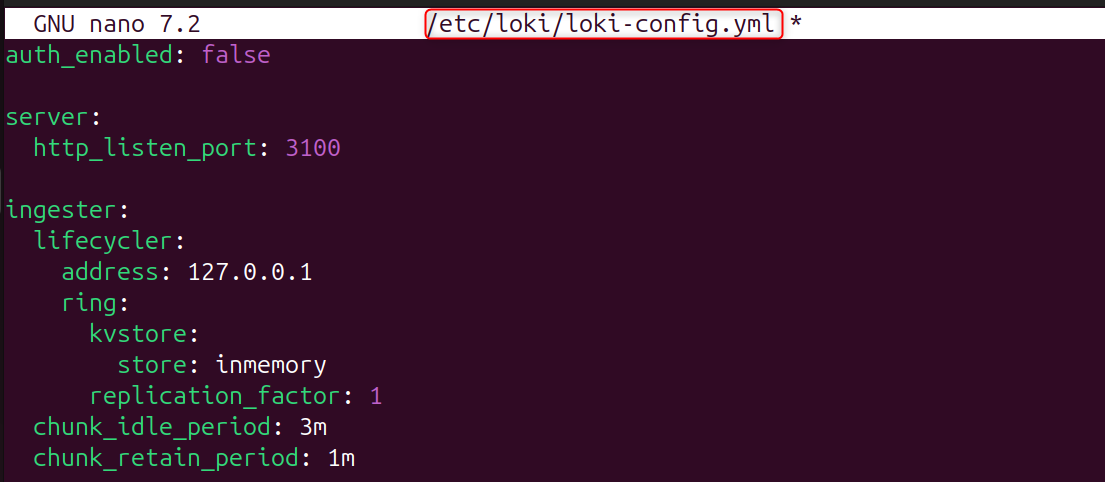
Save and exit.
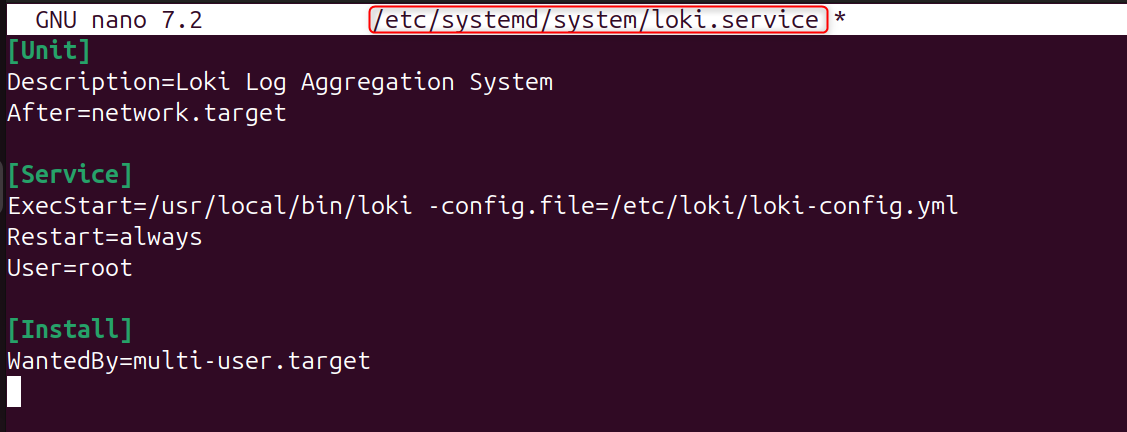
Step 4: Create Loki systemd Service
Allow Loki to be run in the background:
Add:
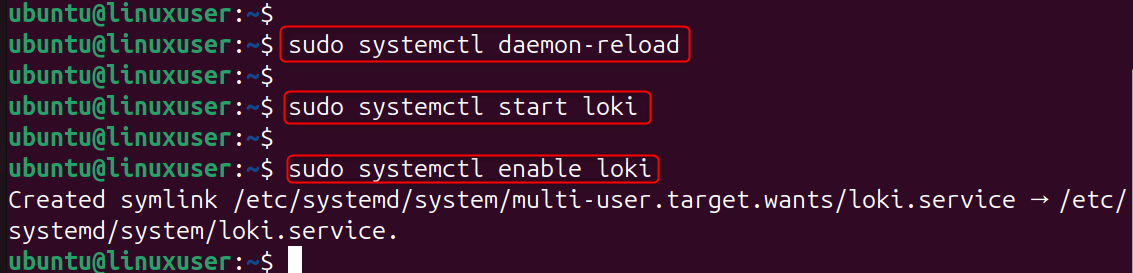
Reload the system:
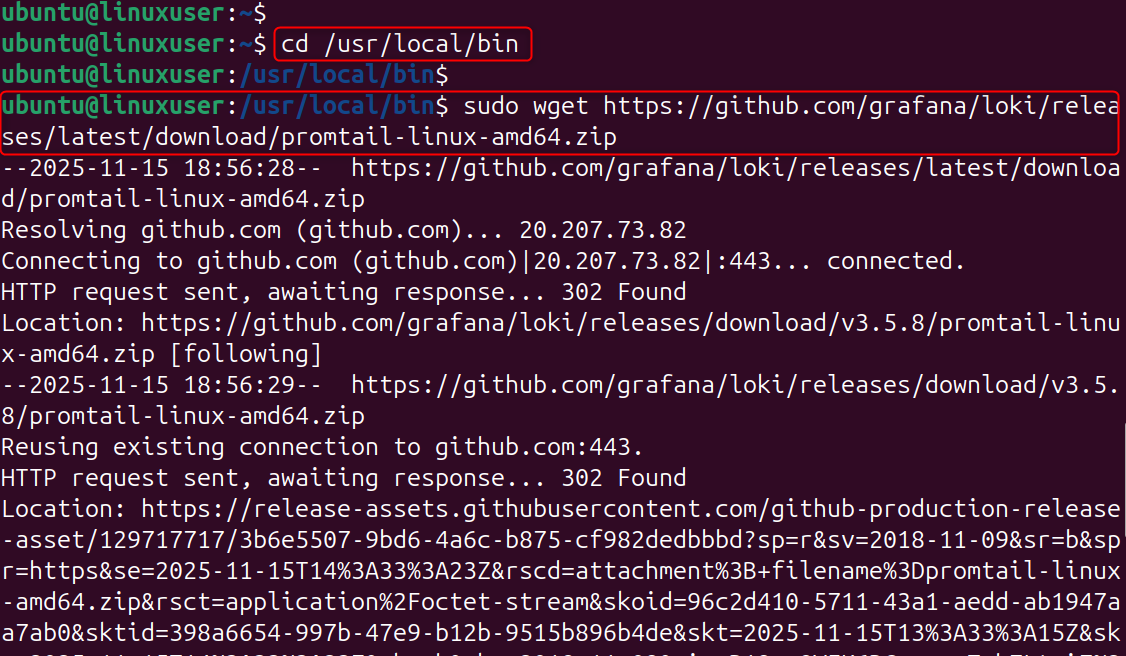
Step 5: Install Promtail (Log Collector)
Promtail sends Loki logs collected from your VPS. Let’s download Promtail:
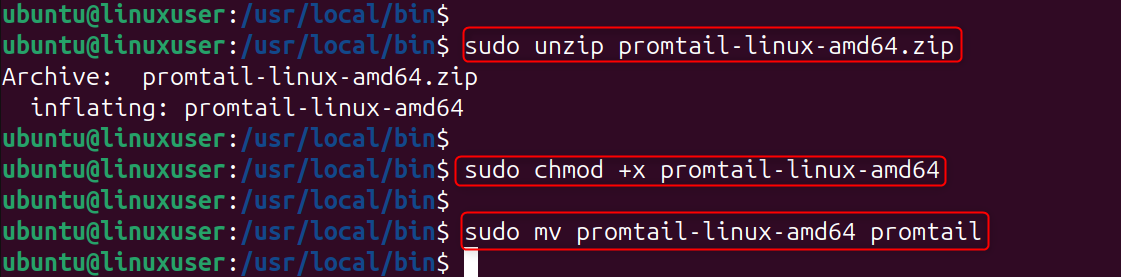
Let’s get the executable permission:
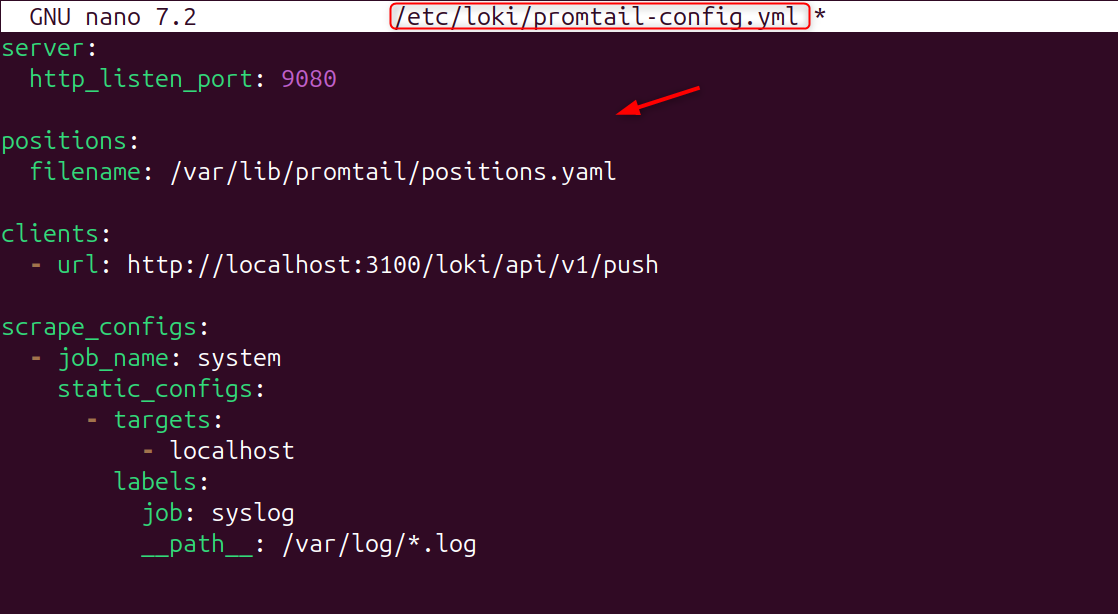
Step 6: Create Promtail Configuration File
Now, create the configuration file:
Paste:
Create the directory:

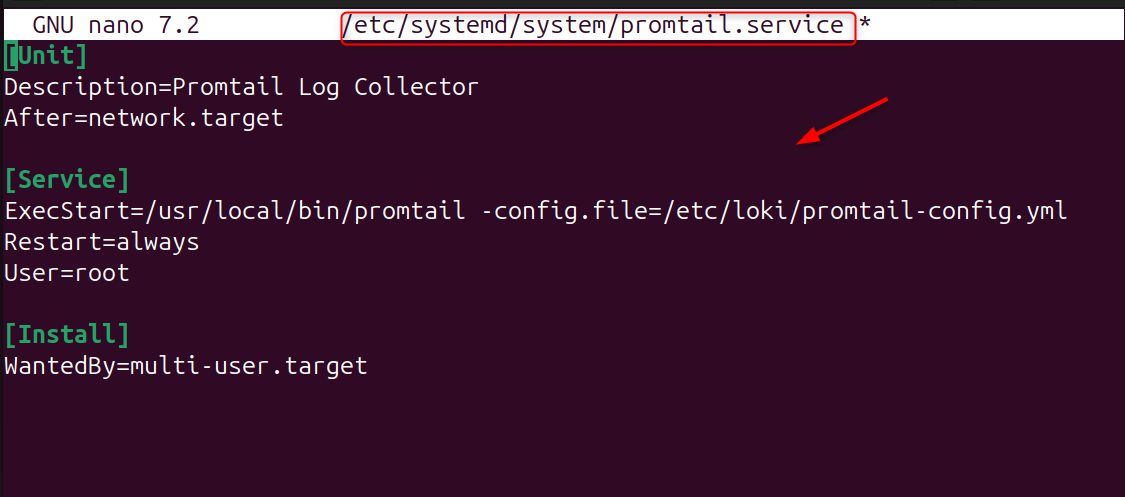
Step 7: Create Promtail systemd Service
Now, create the services:
Add:
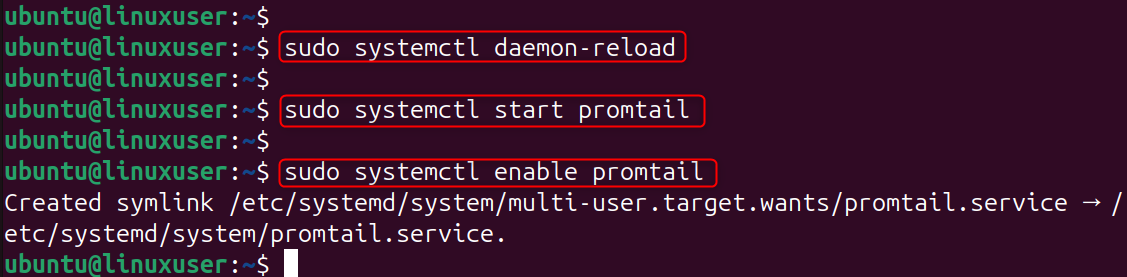
Enable and start:
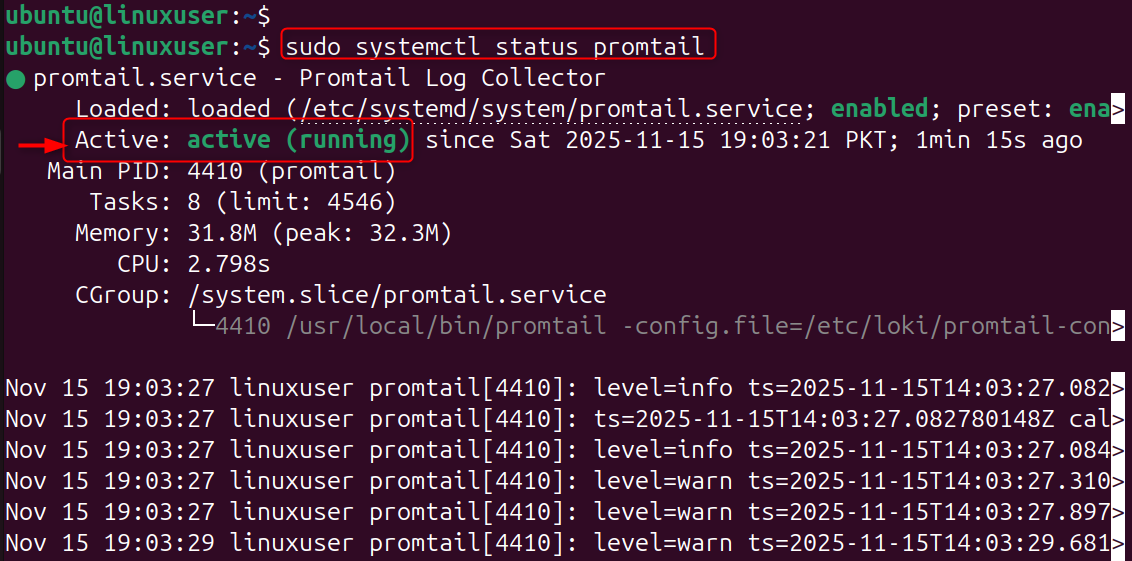
Check status:
Step 8: Install Grafana (Optional but Recommended)
Grafana enables powerful log visualization. Let’s install:
Let’s enable the services of Grafana:
Access Grafana:
Step 9: Test Your Logging Setup
Run a test log:

You should now see live logs streaming from your VPS!
That is all from the guide.
Conclusion
To install Grafana Loki on a Linux VPS for log management, create directories for Loki, download the Loki binary, and place a minimal configuration file in /etc/loki/loki-config.yml, then set up a systemd service to run Loki on port 3100. Install Promtail next by downloading the binary, creating a file that directs logs like /var/log/*.log to Loki, and enabling it as a systemd service. Finally, install Grafana, add Loki as a data source using http://localhost:3100, and start querying logs through Grafana's Explore tab for complete centralized log management on your server.
Do you want to install Grafana Loki on a Linux VPS and manage logs? Consider our Storage VPS solution for your project.